A number of our innovative chemical and life science products contribute to environmental protection. We strive to continuously enhance the sustainability footprint of our products while helping our customers achieve their own sustainability goals.


Energy efficient displays
The Challenge
The danger of serious climate damage has increased in recent years, and many natural resources are growing scarcer. As a result, people are becoming increasingly environmentally conscious, and more and more consumers are taking a product's power rating into account when deciding what to buy.
Displays consume 20% less energy
thanks to liquid crystals for PS-VA technology
How we're helping
Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany develops and markets products that help our customers save energy. Our liquid crystals for PS-VA technology (polymer-stabilized vertical alignment) provide television screens with high contrast while also consuming little energy. They also increase light transmittance, which helps to significantly reduce the amount of backlighting needed - the largest power consumer in a display. In comparison to VA technology, screens with our PS-VA materials consume up to 20% less energy. Furthermore, liquid crystals for PS-VA technology considerably improve image quality. In general, the faster the switching time, the better the image. The polymer-stabilized vertical alignment orients the liquid crystal molecules in a particular direction. The crystals can then tilt faster when they switch directions.
The new UB-FFS technology (ultra-brightness fringe field switching) provides displays with up to 15% more light transmittance than its forerunner, FFS. In combination with other technological developments, UB-FFS lowers end device power consumption by as much as 30%. Furthermore, this new technology also provides superior image resolution and reduces battery size, thereby opening up new design possibilities for product designers.
UB-FFS technology
provides displays with 15% more light transmittance


Smart windows
The Challenge
Climate change and its consequences are already impacting life on Earth today. In the West, 40% of total energy consumption is attributable to buildings, a large portion of which goes to lighting (20%) and air conditioning (15%). With resources becoming ever scarcer and energy prices rising ever higher, companies and private individuals are seeking to boost the energy efficiency of both new as well as existing buildings.
40% of total energy consumption
is attributable to buildings
How we're helping
Under the licrivisionTM brand, Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany is developing liquid crystal mixtures for new applications. For instance, we are working with architects, glass makers and facade manufacturers to create the windows of tomorrow. Our ambitious goal is to use smart windows to make buildings more energy-efficient, thus conserving resources and cutting costs. To this end, we have developed the Liquid Crystal Window Technology. How does this work? At the push of a button, these windows can be darkened within seconds - tinted in whatever color desired. Smart windows thus help regulate the temperature indoors while also setting interior design accents. This technology is made possible thanks to the special properties of our liquid crystals (LCs), which in this case are combined with customized dyes. When a low voltage is applied to the windows, the LCs allow electromagnetic waves, i.e. light, to either pass through, thus making the window transparent, or to be absorbed and blocked, thus darkening the window. In this way, smart windows help regulate the temperature indoors while also setting interior design accents and lowering HVAC costs.
In the Netherlands, we are currently operating a pilot plant for the manufacture of such smart windows, some of which are to be installed in the new Innovation Center under construction in Darmstadt, Germany.
Liquid crystals make windows smarter
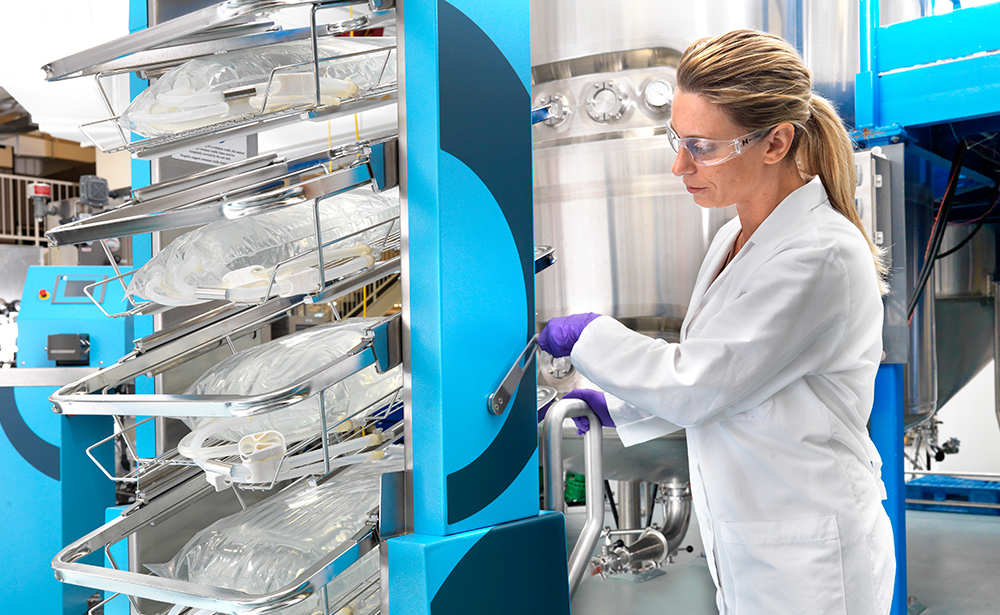
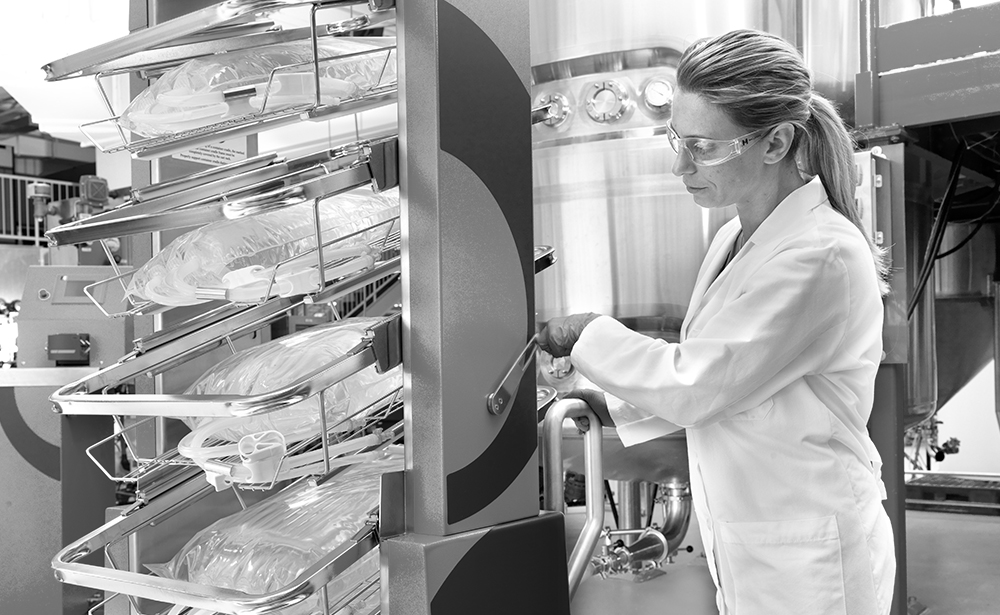


Recycling and waste reduction
The Challenge
Biopharmaceutical production requires many single-use products such as filter cartridges and tubing. However, a lack of disposal options - along with the material properties of the product itself and stringent regulatory requirements - often make it difficult to recycle these items.
54,000 kg of plastic recycled
How we're helping
Through environmentally sound recycling programs, including disposal of used products and packaging, the life science business is working together with its customers to help reduce the environmental impacts of its products and services.
In 2012, Life Science partnered with a waste disposal company and five customers in the United States to jointly pilot a recycling program for biopharmaceutical single-use products. During the ten-month pilot phase, we recycled more than 54,000 kilograms of plastic, which was reprocessed and repurposed into items such as paint buckets and plastic pallets. Non-recyclable components were sent to a cement kiln and used as an alternative fuel source. In 2013, we expanded this program to include two additional customers. Overall, we diverted 189 metric tons of product waste in 2013 and 2014, 91 metric tons of which was plastic that was recycled.
189 metric tons
of product waste diverted
Reducing our customers’ impacts
The Challenge
Just like us, our customers are also striving to conserve resources and protect the environment, which means they expect products from Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany that help them minimize their own environmental impacts.
91% reduction
in autoclave-associated carbon emissions
How we're helping
The life science business has developed the Design for Sustainability (DfS) program, which aims to reduce the environmental impacts of our products across their entire life cycle, from manufacture to end of life. We furthermore work to maximize product performance and ease of use for our customers. Beginning with the concept definition phase, we identify potential environmental impacts, along with opportunities to make improvements.
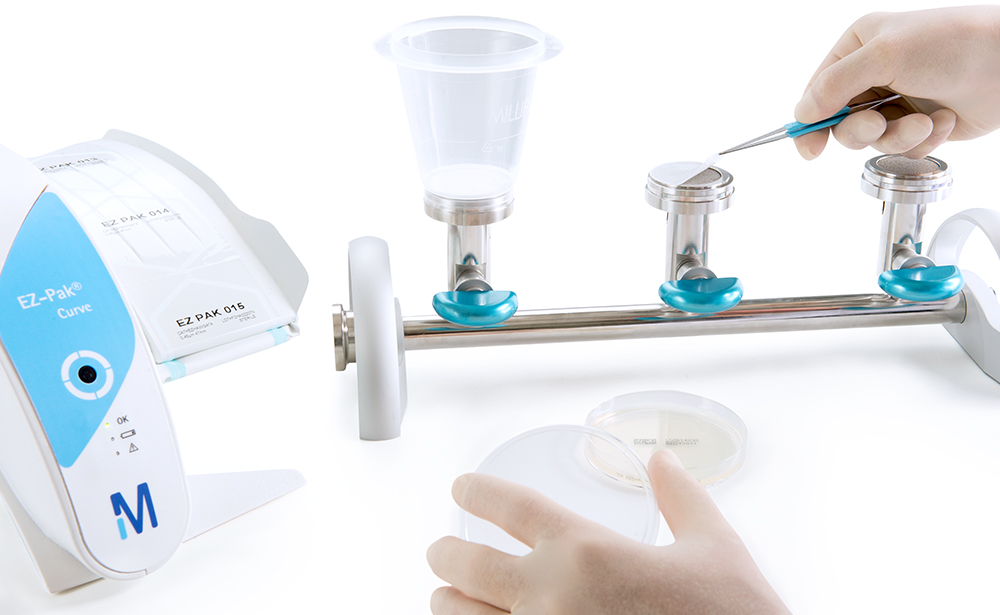
For instance, the life science business employed DfS principles in the design of its new EZ-Fit™ Manifold, which is used for microbiological water testing in the food and beverage industry. In comparison to the previous model, the EZ-Fit™ Manifold is easier to clean, which significantly reduces our customers’ environmental impacts. This device uses 47% less raw material and its packaging consists of 100% recyclable corrugated board. In addition, the filtration heads can be easily removed and autoclaved on their own, unlike the previous model, which had to be completely sterilized. This feature results in an estimated 91% reduction in autoclave-associated carbon emissions.
47% less raw material needed

